Gibb And Dyches 2016 Ieps Free Download

Information Organisation for Monitoring and Managing the Quality of Educational Programs
i
Section of Infocognitive Technologies, Moscow Polytechnic University, 107023 Moscow, Russia
two
Department of Humanities, Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation, 125993 Moscow, Russia
3
Found of Social and Humanitarian Technologies, Moscow State Academy of Technologies and Management Named after K.One thousand. Razumovsky, 109004 Moscow, Russian federation
four
Department of Electrical Equipment and Electric Technologies in the Agro-Industrial Complex, Belgorod State Agricultural Academy Named later on V. Gorin, 308503 Maiskiy, Russia
*
Writer to whom correspondence should be addressed.
Received: 12 December 2020 / Revised: 4 March 2021 / Accepted: 5 March 2021 / Published: 11 March 2021
Abstract
The article explores the issues of the objective approach to managing the educational process assuasive to effectively update and monitor it. The written report is aimed at organizing the processes of command and management of the quality of educational programs with reduced fourth dimension costs. The authors have researched the processes of methodological support of the educational process and the corresponding documents of an educational system. An data system for monitoring and managing the quality of educational programs has been developed. The authors have developed models of the problem surface area, allowing one to make up one's mind the bottlenecks in organizing education quality command. The results of the report are meant for the internal audit of educational services and conveying out the procedures of public command, accreditation, or licensing of an educational organization. They let for the quantitative evaluation of the educational program content and unambiguous interpretation of the obtained result. For this, the authors take developed an objective system for assessing the quality of educational programs. The assessment includes a set of objective indicators with a certain significance: for instance, compliance with certain standards, the use of relevant peer-reviewed literature, agreed forms of education, a point-rating organisation, etc. All criteria are divided into blocks, each of which has a corresponding conformity assessment organisation. The developed assessment scale unifies the quality monitoring procedure, reduces subjective evaluations, and ensures less time-consuming monitoring of the quality of an educational program at the different stages of its life cycle.
ane. Introduction
The footing for the modernization of pedagogy in the Russian federation is formed by ensuring the quality of educational services in accordance with the needs, requests, and expectations of the country, society, and the private [1]. The importance of the quality of education is adamant at the country, regional, and municipal levels, as well as at the level of the system implementing multiple educational programs. Solving the strategic and operational tasks of managing the quality of education requires objective information on the resource, processes, and results of the functioning of an educational organization or its educational directions [2]. In turn, it requires creating and updating the system of monitoring and evaluation of the quality of educational services [3]. The process of creating a system of monitoring and evaluation of the quality of educational services raises the problem of developing algorithms, methods, and the corresponding ways of information support [iv].
The quality of an educational program includes a list of requirements for the educational content considering the accomplishment of scientific and technological progress and international standards, request from a specific consumer and/or customer (due to contest in the labor market, the educational activity organization must exist mobile and dynamic), and the results of internal and external monitoring [5]. A quality assessment system should have a quantitative assessment that allows one to make up one's mind the significance of each of the quality parameters, the level of their influence, and the caste of dependence on each other.
The present study demonstrates theoretical significance since it identifies the primary elements of the regulatory legal component of the educational procedure and its construction and presents an integrated organisation for assessing the quality of the content of an educational plan because various legal and other requirements. The above-mentioned ideas allow for forming a theoretical base of operations for developments in educational process automatization in the spheres of preparing recommendations for students, preparing reporting documents from the teaching staff, and unifying the requirements for internal documentation of various educational organizations.
The applied significance of the study lies in the expeditiousness and objectivity of monitoring educational programs, the reduction of labor expenses for its monitoring and the unification of its content, and the system of unified information infinite of the educational organization with a decreased information back-up [six].
The hypothesis of the written report states that the quality of whatever educational program presents a quantitative value obtained as a consequence of objective evaluation.
two. Literature Review
Russian and strange experience in research in the field of education quality direction comes downward to the following aspects:
i. The development of instruction management technologies and mechanisms. A comprehensive assay of the country of processes is characterized by a diversity of practical inquiry methods [5]. As noted by Tsvelik, the resulting methods do non imply their widespread use in the development of process automatization algorithms [seven]. This is confirmed by Zang and is related to the lack of an unambiguous result of the assay of educational system processes and a generally recognized system of performance indicators for both the educational organization and its structural units [viii].
2. The identification of education direction problems. As noted by Mikhaleva and Tsvelik, research in this area is typically short-term as in Russia an agile reformation of the education system is taking place [vii,9]. Researchers note the need for ensuring the constructive performance of an educational system, the quality of educational services, the competitiveness of educational activity, and the development of science in general [9,ten]. Thus, Liamin points to problems in conclusion-making associated with the contradictory nature of educational services which in essence present inherently socially significant benefits [ten]. Management requires taking into account not only the economic development factors but besides the need to fulfill social obligations [vii].
iii. The development of systems for educational results quality evaluation. The main conclusions of such studies is that modern education is going through an evolutionary transition from the "knowledge" paradigm to the "competency" paradigm [4,11]. Stain, Atkinson, and Al-Gabri country that this transition requires substantial changes both in the methods of educational activity management and the system of evaluation of the results of students. In nearly cases, they are examined from the betoken of psychology and pedagogics [3,12,13].
The research aimed at studying and developing unified approaches, methods, and algorithms for assessing the level of formation of competencies throughout the training is especially worth noting. Such works have a technical profile and simply rely on the results obtained in pedagogical studies to a small-scale extent. They evaluate the volume of data being processed and substantiate the need for developing automated or information systems. In this respect, they advise certain methods and mathematical models for evaluating students' marks obtained equally a result of an academic period [14,15,16].
The developed models (for example, by de Mello, Pedro, Gevorkian, Savenkov, Levitski, Narikbayeva, and Chirtsov) systematize the indicators allowing to determine the level of germination of competencies (or knowledge or skills) in accordance with the developed assessment scale [17,eighteen,19]. The caused models are used for the implementation of algorithms in the software of information or automated systems.
iv. The substantiation of problems of educational organization management are examined from the point of determining the relation between the state and social components [20,21,22,23]. The authors of such studies develop the models of didactics management organization and the methods for assessing the effectiveness of diverse models and their positioning in relation to one some other and create new models of educational organizations. Yet, the results of these studies exercise not make information technology possible to identify constructive management models and the weather of their possible distribution [4,10,24].
Studies focusing on the issues of education management emphasize the development of engineering education. According to these studies, modern engineering pedagogy in Russia does not stand for to the dynamically evolving conditions of the socio-economic and professional environment. The main proposition of such studies is the formation of the respective information and pedagogical environment combining the technologies and principles similar automated learning automated training systems, automated complexes, laboratory inquiry facilities, computer technologies, and educational resource [25,26,27].
Inquiry in this area is aimed at the implementation of information processes in a way that would enable the proper organisation of labor resources and the optimization of network resources and the resources of the fabric and technical back up of the educational process in the process of organizing various forms of learning (including altitude learning) [xi,28,29]. Moreover, the organization of labor resources should exist carried out in such a fashion as to obtain the best results possible to attract financing for an educational organization from various sources.
5. The identification of specific characteristics of educational process support and the formation and evaluation of competencies in the students of an educational system. For example, researchers believe that the formation of students' competencies requires the educational process to exist exercise-oriented [thirty,31]. Scientific studies develop a method of structuring educational textile for improving the do-oriented component of learning. Such works typically lie in the field of pedagogics and are by and large theoretical. These studies upshot in methods allowing i to organize the educational process or the educational material in such a way as to achieve the goal of its mastery by the student. All the same, the technical characteristics required for the realization of the caused study results are not taken into account. The authors note that educational standards and, therefore, educational programs have a weak practical focus. Manufacture employers exercise not possess technologies that allow developing requirements for the level of formation and content of competencies in educational programs [31,32,33,34]. This allows usa to talk most practice-oriented educational activity. Most often, educational organizations draw upward curricula for several years in advance, without changing them for a specific flow of student learning. This is a serious problem, since the modern educational market is dynamic and technology is changing rapidly. Thus, upon completion of the training, the specialist is not ready to perform the work assigned to them at the level that has formed in the industry. This state of affairs is typical not simply for most Russian just also foreign educational institutions. Burlea-Schiopoiu notes that the connectedness between curricula and the industry should be strengthened (based on the instance of student accountants) [35,36].
Some other office of scientific works focuses on the study of altitude learning and the specific characteristics of developing electronic educational resources. Active attempts at developing electronic educational resources are made both in Russia and in strange countries, although the accumulated experience and the obtained results are not systematized. Electronic learning tools duplicate the content of the traditional ones and virtually educational organizations practise not have an idea of how to effectively implement the available resource in their activities [19,37].
The subjects of the educational activity (mostly teachers but too students) typically acquaintance the automatization of said activity with the attempts to standardize the educational procedure, abandon the individual approach, and completely replace the teacher. This is the cosmos of the data support of the educational process. There are few software environments and shells aimed at creating interactive electronic educational resources for basic disciplines [38,39,40].
6. Increase in the demand for educational services and the demand for graduates of educational institutions. Researchers have adult the models and methods for predicting the demand for staffing. Some studies examine this issue from the point of recruitment of applicants bookkeeping for the need in the educational services market and the demand of the regional economic system in the labor market [41,42,43]. Zang, Al-Gabri, and Işık note that each educational organization develops its methods of resolving this problem [eight,13,44]. Research in this area is typically sociological or psychological. Nevertheless, the acquired applied results are formalized poorly and the responsible managers make the decisions on the realization of bidder attraction programs based on their experience rather than with the utilize of automatic determination support tools [three,45,46].
Summing up the literature analysis, the experience acquired in the sphere of educational process organisation has high theoretical and practical significance, but the individual educational process elements are viewed in it equally contained objects isolated from the educational organization [47,48,49] or educational processes [50,51,52]. Nosotros conclude that the results of the wide diversity of inquiry in the sphere of education are democratic and do non unite into one system. The integration of the obtained results allows creating a unmarried arrangement with consistent and relevant data, available both to scientists or experts for new research and to terminate users—all participants in the educational process.
3. Methods
3.1. Enquiry Blueprint and Hypothesis
The evolution of algorithms of the information system'due south functioning requires determining the specific features of the work of specialists that execute the educational program quality control. As part of the written report, we developed questionnaires and interviewed methodologists of educational organizations, department heads, experts in public control of the quality of teaching, experts in professional and public accreditation and independent assessment of qualifications, and researchers of the Found for the Development of Education of the Russian University of Teaching [53]. Their number was eight, which corresponds to the ratio of the confidence indicators of the obtained issue and the maximum permissible mistake of the standard departure share before the outset of the survey. Interviewing was carried out orally with recording in special forms of answers. This was done during the accreditation procedure of the educational organisation and then that the expert could not simply answer the question but also demonstrate the actions they performed, as well equally, if necessary, explain them.
Each specialist answered a prepare of questions determining of import factors of the inspect of the educational plan content. Such questions included:
-
How much fourth dimension (on boilerplate) does it take you to evaluate one document?
-
What elements of the document under evaluation are important (conform in descending order: title folio, references, competencies, cess tools, weather condition for implementation, distribution of the number of teaching hours, didactic units, etc.)?
-
Practise you consider the presented fragment of the educational plan content a mistake? Explain your decision.
The answers obtained as a result of interviews arrive possible to formalize the work of specialists executing the control of the educational program content. This stage of the report allowed the states to identify:
-
the stages of evaluation;
-
the fragments of documents the specialists focus on;
-
the time required to evaluate the separate sections of a document and the whole document;
-
the importance of the elements of the educational program content;
-
the composition of the reference material and the timing of its use.
This effect allows for developing a universal algorithm of educational program evaluation for high-quality automatization of the largest number of stages of this work.
The presented method was important and labor-intensive. Preparing interview questions, developing survey content, choosing the time and identify for working with experts, and processing and interpreting the acquired results were the steps cardinal to this method and its importance is hard to overestimate. This allows one to understand the methodology for checking the content of educational programs, determine the significance of each element of its content, etc. Equally a event, we determined non only the algorithms of work but besides tested the reliability and randomness of the acquired results, established the optimal and minimal number of experts that have to be recruited for the development of the criterion and evaluation complex of the educational program. This stride was the i making all further stages of the study possible. The results are necessary for the implementation of the method of expert assessments, which makes it possible to obtain the weight values of each criterion for the assessment complex of the information system. The results are the footing for drawing upwardly formal models presented in the Results department of this article.
3.2. Data Collection and Processing
The study uses the method of structural analysis to formalize aspects of the trouble surface area. The main goal of structural analysis is the transformation of general, imprecise noesis most the original problem area into verbal models describing the subsystems of the modeled processes or objects. The implementation of this method allows to:
-
identify all the subjects participating in the procedure of the inspect of the educational program content;
-
establish the key objects of processes;
-
identify the relations betwixt objects and processes;
-
determine the methods and means of information system modeling.
The acquired results are presented in the course of graphic models:
- (a)
-
Euler diagrams demonstrating the relations between the objects of the subject. In the study, these diagrams allow us to illustrate the influence of documents and requests on the content of an educational program, the relations betwixt the educational program elements, etc.
- (b)
-
Directed graphs demonstrating the links betwixt the key elements of an educational program. The presence of links between elements allows determining their subordination, isolation levels, and possible iterations of algorithms for evaluating the content of an educational plan.
- (c)
-
Effect-driven procedure chains assuasive us to visualize the sequence of events and actions, their participants, performers, and document flows. This type of model illustrates the specific characteristics of interactions between all process subjects in using an information system. Said subjects include information arrangement modules, specialists of an educational organization, and files necessary to execute processes and obtained as a result of completing them.
- (d)
-
Radar charts demonstrating the interdependence of numerous values. This approach is used for demonstrating the results of educational plan content evaluation. The values marked in the coordinate system correspond to the assessments of the aspects of the educational plan quality criteria. The values of the aspects are determined by the information arrangement automatically according to the developed algorithms.
Later structural analysis, we obtained an array of elements that define the key aspects of the content of any educational plan. The interviewed experts were tasked to range these elements. To do this, they were asked to fill up out questionnaires, where all objects are grouped in structural blocks by certain characteristics [54]. Thus, the method of adept assessments is implemented. The implementation of this method results in criterion an evaluation complex of an educational program consisting of criteria and their aspects. Each criterion and aspect has its significance value. The acquired evaluation results are tested for consistency beyond unlike experts [55] using Kendall's coefficient of cyclopedia (Formula (1)).
where W—coefficient of concordance of experts on the structural element in question;
S—the sum of squared deviations from the mean;
1000—the number of experts;
n—the sample size (the number of items evaluated);
Ti —the number of ties (types of repeating elements) in the set of ranks for expert i.
To ensure that the obtained coefficient W is not random and the obtained result is reliable, its significance is tested [55] using Pearson's chi-squared test χii calculated by Formula (ii).
To make up one's mind the significance of experts' consistency in assessing the aspects, we used significance level α = 0.05. The significance level used for determining the consistency in the assessment of criteria was α = 0.01.
Storage and processing of the received information and their use for the functioning of an information system crave a database. The pattern of the database structure must preserve the balance between the functioning of the data organization and the integrity of the stored data. For this, methods of the theory of relational databases are used. The database is normalized based on the discipline area and the technical capacities of potential clients. As a result of the implementation of methods for relational database design, an entity–relationship model (ER model) was obtained. The ER model allows the states to realize all the capabilities of the information organization implied past the goal and objectives of the study.
4. Results
The educational process is regulated by numerous federal and regional regulatory documents and the local documents of a specific educational organization. Figure 1 presents a list of documents affecting the content of an educational program.
This model reflects the results of a alter in the approach to education in Russia that has occurred over the past five years. The main approach to training now is the use of practice-oriented methods meeting the employer'southward needs. Therefore, a divide cake should exist allocated to documents, the content of which is determined by external organizations.
Whatsoever educational program must comply not just with an educational standard, which may not change over the years merely also, for example, with professional person standards that define the labor functions of modern professions and industry specialists. The constantly changing approaches and content of practice-oriented and demonstration exams according to World Skills standards oblige an educational organisation to consider these facts in the content of implemented educational programs.
An educational program has a clear structure regardless of the educational organization or the educational direction. The conducted study allows us to establish the key elements of this structure and their interrelation. These results are presented in Figure 2.
If every element of an educational program is formed, it can be concluded that the educational program is compiled correctly. Thus, the basis of the criterion and evaluation complex is formed by the structural elements of the educational program (criteria). Each criterion comprises certain aspects.
The lists of aspects and possible mistakes in its content were obtained equally a outcome of studying the results of the survey and interviews of specialists participating in the expert evaluation of the quality of the provided educational services. All possible errors in the educational program can be classified as follows:
-
Higher-guild mistakes (category 1) arising from non-compliance with the requirements of regulatory documents (educational and professional standards, laws on education, etc.).
-
Middle-society mistakes (category 2) appearing in the text of an educational program due to not-compliance with the requirements of the documents of the educational arrangement (academic plans, competency matrices, etc.).
-
Lower-club mistakes (category iii) emerging as a result of not following the educational plan file layout template.
-
Content mistakes (category 4)—mistakes made in the formation of didactic units (topics practice not stand for to the academic discipline, the recommended literature does not allow studying the declared topics, etc.).
-
Technical mistakes (category five)—mistakes made by the typesetter when typing due to abandon or depression level of proficiency in the software.
Mistakes belonging to category four tin be checked through the developed data system. The content of the topics of bookish disciplines is attributed to the creative role of the educational program. For various reasons, every teacher tin view the substantial role of the programme in their own manner. Such reasons can include:
-
the teacher's professional level;
-
the textile and technical base of the educational organisation;
-
the level of students' training;
-
lobbying the interests of the educational system, industrial partners, or political actors.
Therefore, this role of an educational program has to be evaluated by a specialist. The evaluation of aspects of this benchmark tin can be formed based on the conclusion of the head of the educational program, external reviewers, and the conclusion post-obit the meeting of the department or kinesthesia council.
The remaining categories of mistakes can be identified automatically without the back up of a specialist. In one case the file of the educational program (or its separate parts) is uploaded, the algorithms of the developed information organisation can autonomously conduct the cess past the aspects of criteria implying the possibility of mistakes from categories ane–3 and category 5 and provide access to responsible specialists to cheque for errors from category 4. After the evaluation is completed, the system calculates indicators based on the assessment rules determined by the criterion and evaluation complex. A part of the criteria and their aspects is presented in Table 1.
The indicators presented in Table i were obtained using the expert assessment method based on the results obtained in the procedure of interviewing and questioning specialists participating in the examination of educational programs' content.
The structure of such an information system is presented in general form in Effigy 3.
The information arrangement for monitoring the quality of educational programs comprises the following modules:
-
Converter. Allows for converting file formats into the ones used by the respective system modules (for case, a pdf file of an educational program and the list of criteria must be converted to XML).
-
Import/Export. Input/output of the parts of files for the correct operation of modules of the current system or external systems.
-
Assessment of aspects/criteria. Determine all categories of mistakes in the formal role of the educational programme or its parts.
-
Control. Forms the list of experts for evaluating the categories of mistakes from the creative part of the educational plan or its parts, provides access to assessment materials, and records the received expert answers.
-
Monitoring. Allows u.s.a. to suit the parameters of scales for assessing the aspects, criteria, or the integral indicator, catechumen the principal result of the assessment of aspects and criteria into a result corresponding to a certain scale, and course a listing of recommendations for corrections.
-
Statistics. Records the acquired results and allows creating reports on the given parameters.
-
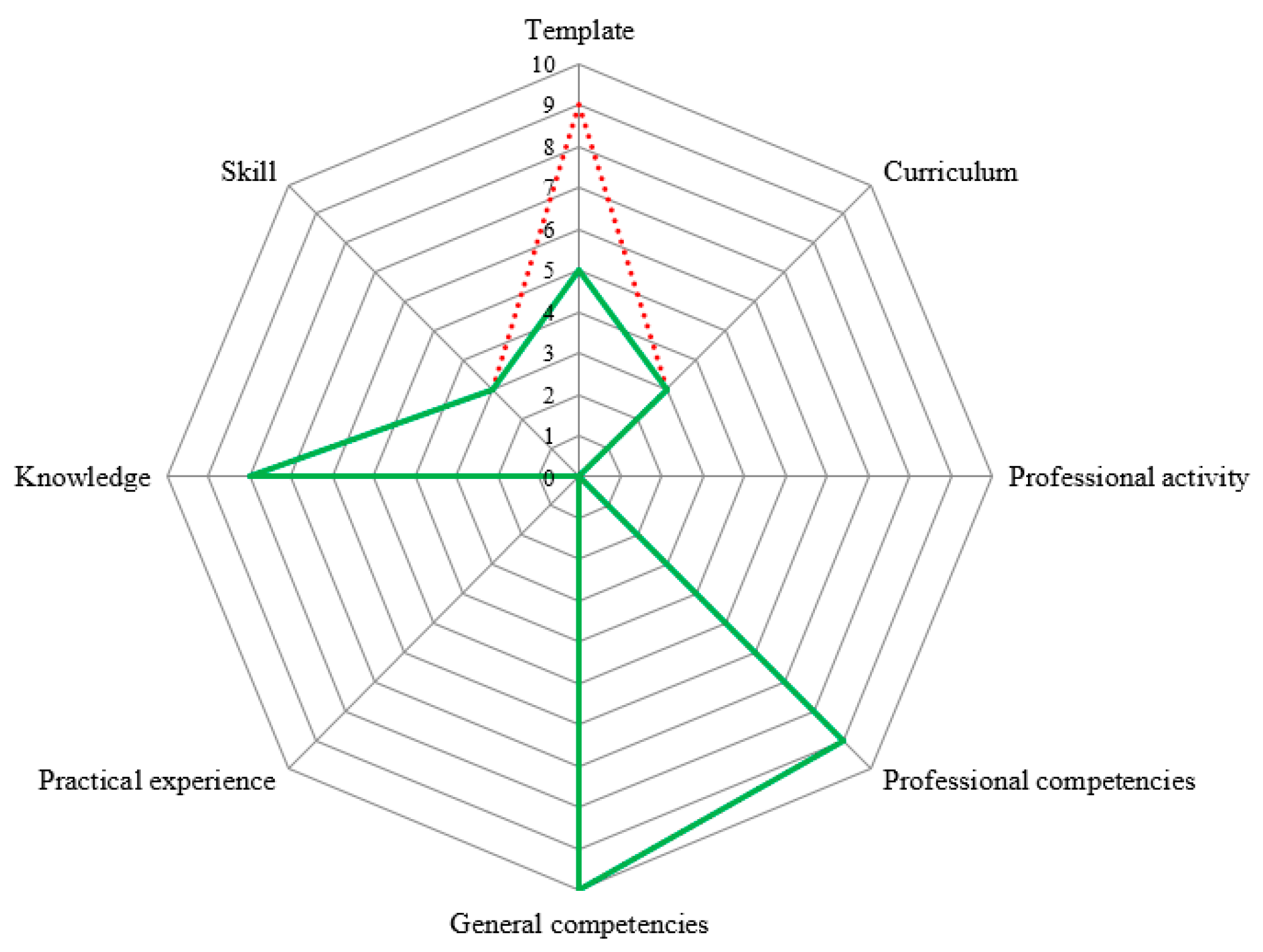
Designer. Creates diagrams based on the given parameters or the created reports (an example of such a diagram is presented in Figure 4).
-
"Monitoring" Database. Stores reference files, report files, and other data necessary for the functioning of the information system (an ER model of data is presented in Figure v).
Effigy six demonstrates a model of the process of interaction of a teacher with the information system to obtain the results of the cess of the formal part of the operational program of field of study.
The obtained model of an data system allows one to exclude the human factor equally much equally possible when checking the content of the educational program. Information technology is possible to rapidly obtain a list of recommendations for correction and keep documents upwardly to date. The resulting construction of the information system corresponds to the accustomed hypothesis.
five. Give-and-take: Data System for Education Programme, and Open Innovation
5.1. Discussion: Information Arrangement for Managing the Quality of Eudcational Program
Any educational organization has to ensure the interaction of iii master processes: obtaining resources, using them to attain the goals of the educational organization, and transferring the results of work to the external surround. The organisation of pedagogy quality management has to accept into account the pattern of interactions betwixt diverse authorities the interests of which prevarication in the field of education [14,56]. The following characteristics are considered as the components of the quality of education: quality, motivation, and achievements of the teaching staff, the state of the cloth and technical base of an educational organization, the quality of educational programs, the quality of students' knowledge, the composition of students, the introduction of innovations, the demand for the organization'south graduates in the labor market, the achievements of students and graduates, the innovative activeness of the heads of an educational system [14]. Thus, the quality of pedagogy tin be viewed as a multifaceted concept and studying information technology requires the complex process arroyo.
The circuitous approach to studying the problem of the quality of education tin can significantly reduce the time and financial expenses of organizing the educational process and lower the degree to which the human factor affects the obtained results. The conducted studies practise not demonstrate satisfactory results in determining the relations betwixt the indicators of the state of educational programs, the educational process, and the system of the work of the teaching staff. The existing methods are not oriented on operational management in improving the quality of educational activity, organizing the cocky-control of the education staff, predicting the development of an educational management, and the objective assessment of the obtained results [57,58].
The results attained in the present report have not only theoretical but likewise applied significance. The reliability of the conducted research and the validity of the acquired results are ensured by the correct use of research methods, the approbation of various aspects of the piece of work at scientific and practical conferences, obtaining the certificates of state registration of a software product, and the implementation of the benchmark and evaluation complex in several educational organizations [6,55]. The functioning of the developed information organization involves phased execution of the operations the results of which can exist corrected. The stages of the information arrangement performance include determining the limerick of experts ↑, establishing the value of aspects and criteria ↑, obtaining an educational program for evaluation, evaluating the aspects and criteria, forming the recommendations and the final effect, output of the terminal event, and notifying the specialists about the results of the assessment [6]. The arrow symbol (↑) marks the stages allowing corrections to exist made. The presented approach meets the requirements of the quality loop of the educational process.
A significant difference can be detected when comparing the results of educational program evaluation conducted using the ways of the developed data system and manually.
Studies in the area of statistical assessment of the quality of typing demonstrate that when processing text, there are always mistakes [59], the number of which a regular flow [37]. However the proofreading procedure does not completely prevent errors only reducing their number [lx,61]. The number of mistakes depends on feel with both texts and text editors. Specialists, monitoring the content of educational programs are not especially trained in the sphere of publishing. Moreover, the volumes of the documentation being evaluated are estimated in hundreds of pages, requiring constantly referencing other documents or reference materials. Thus, high-quality monitoring of the educational program content either becomes highly time-consuming or becomes faster due to the adoption of the formal approach to the evaluation of private documents.
The developed data system quickly finishes the evaluation chore: the specialist only needs to upload the source file and wait for the consequence. However, information technology should be borne in mind that only the formal indicators of the educational program are assessed in the specified time, the evaluation of the creative role occurs simultaneously. Thus, the load is evenly distributed, increasing the fourth dimension for classes and enquiry and methodical piece of work.
The mod studies conducted in the sphere of education allow practical implementation of the results presented in them only in the management of human being resource, the assessment of the development of educational textile, or the automatization of certain types of activities of structural divisions of educational organizations [twoscore]. The obtained results focus on convenience, personality development, and students' education from the point of psychology and pedagogics. Meanwhile, the developments aimed at the automatization of the work of the teaching staff or other specialists related to the methodical support of the educational process provide additional workload [22,30,38]. The caused results can exist applied to specific educational organizations in which the report is conducted. This conclusion is related to the fact that every educational organization has the correct to regulate the content of the educational process independently. Moreover, even two educational organizations of the same region with the same direction of training will differ in the content of educational programs. If we examine educational organizations not merely from the point of the content of educational programs but besides from the point of the educational procedure, the differences become even more acute.
5.2. Discussion: Information Arrangement, and the Open Innovation in Educational activity
The concept adult within the framework of the written report provides an open innovative approach to education in terms of using the information arrangement to make up one's mind the quality of educational programs. The adult information organization provides the continuity of management and the consistency and interconnection of individual educational processes, as well as their interaction [62]. With an open up innovative arroyo, educational organizations can interact with each other to develop common quality criteria, utilise targeted knowledge flows, and place promising ideas or developments for further mutual apply. The system of education quality management has to exist integrated and focus on modern data technologies the implementation of which has to be assessed through both qualitative and quantitative indicators. Such indicators should be developed not only within educational organizations (or between them), just with the involvement of industrial partners. Industrial partners should participate in determining the development trajectory of any educational program, ensuring, amidst other things, culture of dynamics of open innovations in education.
Changes in the criteria or content of an educational programme (including whatever educational processes) should occur only upon completion of the full training bicycle. This makes it possible to appraise the effectiveness of each process and decide its macrodynamics in the instruction system, instruction, and industry innovations, every bit well as the microdynamics of the processes themselves within the educational organization. The criterion and evaluation complex developed in the form of this study are "flexible" and easily adjustable, meeting the requirements of an open up innovative arroyo. Moreover, the results acquired in different educational organizations will be relevant and can be used for integrated management of the education system not merely at the level of a specific region only as well across the country [3,58].
The adult information organization for monitoring and control of the quality of educational programs takes into account both the specific characteristics of the educational system and a wide variety of other external factors influencing the content of the educational program. This advantage is achieved through the use of information system modules. Studies demonstrate that to achieve constructive management, obtain the desired result, and adapt the system to various kinds of external changes, it is required to use a modular structure of software tools. The same refers to educational organizations. Equally demonstrated by the studies in the field of informatization and automatization of educational activity, individual modules of the developed information systems allow to determine the level of germination of students' competencies, gather and process statistical information on their performance, make up one's mind the levels of noesis or the effectiveness of the piece of work of the education staff of the educational organisation, plan lessons, identify the gaps in students' noesis, plan the load of independent piece of work, improve the methods of teaching and testing students' knowledge, etc. The resulting data organization does non exclude the developed modules or distort the results obtained at the output of each information system. On the contrary, it serves as a means that would allow combining the developed information systems or their split modules equally much as possible to design a unified information system of the educational organization [14,31]. This makes it possible to ensure the availability of open up innovation between higher education and any branch of the national economy (for instance, industry, tourism, etc.).
Every bit a event of the study, it was established that the educational process is complex and comprises a neat number of interrelated objects, with data flows emerging between them, control actions, etc. The chief object of the educational process is the educational programme. Studies related to the educational process organization annotation that the educational program consists of heterogeneous information that needs to be systematized via special methods. In addition, the process of accumulating and updating said information has to be continuous [59,60]. This requirement is supported by the results of our study. Meanwhile, the structural links between the elements of the educational program and the documents allowing to comport out continuous monitoring of its content are established.
vi. Conclusions
As a result of the enquiry, we developed a universal model of the information organisation. It allows united states to acquire objective evaluation results, promptly brand changes to its construction, keep the educational programs upwards-to-appointment, and inform and take corrective actions in managing the procedure of developing regulatory documents of an educational system. This presents an important part of the educational procedure since educational standards, the requirements and demands of the industry, the teaching staff, educational and reference literature, and fabric and technical back up of the educational process modify almost annually. For a specialist to decide to improve the quality of an educational program, it is necessary to consider numerous factors that can be unapparent or subjective. The conducted analysis of the educational process support processes demonstrated that educational organizations currently use software tools that work autonomously from each other. Moreover, even if the results of the work of i system are used in some other one, data consign or import is executed manually with the adjustment of additional parameters. Therefore, operational management largely depends on the human cistron: the level of proficiency in the software demonstrated by specialists administering the corresponding systems and their personal interest in obtaining the effect. To enable the customization and scaling of the adult information organisation, procedure models that let for showing the key objects, and the relationships between them, have been created. A visual sit-in allows ane to evaluate the bottlenecks, equally well as the possible options for their modernization. The structural approach enables quick adaptation to the changes in the external environs. The in a higher place-mentioned model serves as a basis for the formation of the criterion and evaluation complex lying at the base of operations of the information system for monitoring and managing the quality of educational programs. The developed structure of such a system is "flexible" and allows 1 to arrange the parameters of the criterion and evaluation complex and determine the values of parameters and the degree of their importance. All of these adjustments require minimal participation of specialists in the procedure of educational programme content evaluation. The resulting data system presents an independent unit of the textile and technical base of an educational system; still, it is also an element that unites several heterogeneous information systems. Thus, an integrated data organization ensuring the exhaustive and competitive performance of an educational organization in mod market place conditions is created.
Summing upwardly the conducted study, nosotros can argue that its objectives were completed and the goal was accomplished. The formulated hypothesis was confirmed.
The directions for farther research that should be noted include farther comeback of the objectivity of the educational program content evaluation, the development of algorithms for automated formation of the content of individual elements of the educational program content, and the comeback of the algorithms for educational plan content evaluation to reduce the corporeality of fourth dimension it takes.
7. Research Limitations
The methods used in the inquiry are universal and generally accustomed. During the study, nosotros did not have any difficulties in using them and interpreting the results. The developed algorithms allow for creating an evaluation method for educational programs in different study areas and an information arrangement based on information technology. Such software is a powerful tool in the hands of the participants in the educational process involved in its provision and control. The criterion-cess complex is customizable and allows one to modify not just the number of criteria or involved processes, but also experts. The mathematical apparatus used allows maintaining the model in a consistent land. The model of an information arrangement makes it possible to unambiguously process any input data and obtain a consequence based on those indicators that are embedded in it past an educational organization or any other specialized department. This indisputable advantage allows the model to exist used both in the Russian educational activity arrangement and away.
In conclusion, we did not set a goal to develop an optimal model of the system, but to reduce the costs of implementing certain processes in the field of educational activity quality direction. At this phase, the goal has been achieved. We admit that with the farther development of this topic, the utilise of new software tools will farther reduce certain categories of costs.
Author Contributions
M.S.L.—study design, structural analysis, and formalization of models, writing the main body of the article. N.A.O.—report design, interpretation of the caused results. T.N.Due south.—information collection, formulation of the problem, goal, objectives, and hypothesis of the study. Southward.South.—literature review, interpretation of the acquired results. Southward.F.V.—statistical data analysis, estimation of the acquired results. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Non applicative.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the written report.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available on request from the respective author.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to Anna Ivanovna Guseva, medico of technical sciences, professor of the Federal State Democratic Educational Establishment of Higher Education "National Inquiry Nuclear University MEPhI", Iurii Nikolaevich Samarin, doctor of technical sciences, professor of the Moscow Polytechnic Academy, and Galina Viktorovna Tkacheva, candidate of pedagogics, corresponding fellow member of the University of Professional Education for their objective evaluation of the conducted work, useful advice on organizing and conducting the experiments, interpretation of the caused results, and comprehensive support.
Conflicts of Involvement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Osipova, Due east.A. Comprehensive Cess of the Quality of Education as a Condition for the Development of the Regional Educational System. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Educational activity Evolution of Irkutsk Region, Irkutsk, Russia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Poliakova, A.South. Commonage Methods of Data Mining Based On Fuzzy Logic. Ph.D. Thesis, Reshetnev Siberian State Academy of Science and Technology, Krasnoyarsk, Russia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Stain, D.A. Qualification-Oriented Expert Arrangement for Managing Academy Educational Process. Ph.D. Thesis, South Ural State Academy, Chelyabinsk, Russia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov, A.A. Mathematical and Software Back up of the Organisation of Assessing Educational Results at a University Taking into Account the Non-Linearity of the Learning Procedure. Ph.D. Thesis, Perm National Research Polytechnic University, Perm, Russia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Korovina, L.Five. Model and Algorithms for the Analysis of Organisation Management Documentation. Ph.D. Thesis, Penza State Academy, Penza, Russian federation, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Logachev, M.S. Construction, Methodology, and Algorithms for the Performance of the Educational Programs' Quality Monitoring System. Ph.D. Thesis, Moscow Polytechnic University, Moscow, Russia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tsvelik, Eastward.A. Method for Constructive Direction of University Educational Programs. Ph.D. Thesis, Volgograd State Technical Academy, Volgograd, Russia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, L.5.K. Models and Algorithms for Managing the Quality of Foreign Students' Preparation Based on Intellectual Controlling Methods. Ph.D. Thesis, Voronezh Country Technical University, Voronezh, Russia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhaleva, O.A. Mathematical and Software Support for Processing the Results of Group Assessment for Managing Network Expertise in a Distributed Environment. Ph.D. Thesis, Bryansk Country Technical University, Bryansk, Russia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liamin, A.V. Models, Methods, and Algorithms for Designing Automatic Control Systems for the East-Learning Process in Higher Teaching. Ph.D. Thesis, ITMO University, Saint petersburg, Russia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Burmistrova, East.V. Methods and Algorithms for Monitoring and Evaluation of the Quality of Educational Services at a University. Ph.D. Thesis, Novosibirsk State Technical Academy, Novosibirsk, Russia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, R.D. Why the current teaching reform strategy won't work. Bug Sci. Technol. 2012, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Gabri, Five.M. Data Support and Management of the Process of Intermediate Certification at a University. Ph.D. Thesis, Don State Technical University, Rostov-on-Don, Russian federation, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tigina, 1000.Southward. Automatic Arrangement for Assessing the Level of Competence Germination amidst Students throughout the Training. Ph.D. Thesis, Moscow Country University of Printing Arts, Moscow, Russia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Isip, G.I.Thousand.; Li, R.C. A Hierarchical Model of Service Quality in College Education Institutions. Ind. Eng. Manag. Syst. 2017, 16, 632–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Thousand.G.; Edwards, K.East.; Tweedy, J.F.; Lichterman, H.; Knerr, A.R. The Curricular Arroyo to Student Diplomacy: A Revolutionary Shift for Learning across the Classroom; Stylus Publishing: Sterling, VA, Us, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- de Mello, K.B.; Pedro, Westward.J.A. Quality of Piece of work Life Programs Management in Higher Instruction Public Institutions. Rev. Cienc. Hum. Da Univ. Taubate 2017, 2, 89–99. [Google Scholar]
- Gevorkian, E.N.; Savenkov, A.I.; Levitski, Thou.Fifty.; Narikbayeva, Fifty. Modernization of the Management of a University Educational Structural Unit of measurement Based on the Distributed Leadership Model. In Proceedings of the Theory and Practice of Project Management in Education: Horizons and Risks: International Scientific and Practical Conference; Ryabov, 5.V., Ed.; SHS Spider web of Conferences: Moscow, Russia, 17 April 2020; Volume 79, p. 02008. [Google Scholar]
- Chirtsov, A.S. Methods and Tools for the Automatization of the Evolution of Electronic Educational Resources for the Variable Study of Physics. Ph.D. Thesis, ITMO University, Saint petersburg, Russia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bulla, C.; Hunshal, B.; Mehta, S. Adoption of Cloud Computing in Educational activity Organisation: A Survey. IJESC 2016, six, 63–75. [Google Scholar]
- Daddow, A.; Cronshaw, D.; Daddow, Northward.; Sandy, R. Hopeful Cross-Cultural Encounters to Support Educatee Well-Existence and Graduate Attributes in College Pedagogy. J. Stud. Int. Educ. 2020, 24, 474–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire Seoane, M.J.; Bermúdez, B.Fifty.; Montes, C.P. Perfiles de empleabilidad: El caso de una Universidad española. Cuad. Econ. 2020, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.Due east.; Hoelscher, 1000.J. Pedagogy, co-published with: A.C. In Managing Diversity Flashpoints in Higher Education; Rowman and Littlefield Publishers: Plymouth, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Katılmış, A. Values Instruction as Perceived past Social Studies Teachers in Objective and Practice Dimensions. Educ. Sci. Theory Pract. 2017, 17, 1231–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, M.A.O.; Rueda, Eastward.C.; Castillejos, O.G. Evaluation and accreditation processes in educational programs at the Autonomous University of Chiapas, Mexico. ATENAS 2016, 36, 102–118. [Google Scholar]
- Le, N.-T. A Classification of Adaptive Feedback in Educational Systems for Programming. Systems 2016, iv, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduaran, A. Influence of Students' Feedback on the Quality of Adult Higher Distance Education Service Commitment. Turk. Online J. Distance Educ. 2017, xviii, 160–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda Fernández, J. Análisis del desarrollo de los nuevos títulos de Grado basados en competencias y adaptados al Espacio Europeo de Educación Superior (EEES). REDU. Rev. Docencia Univ. 2016, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, J.50.; Sanders, J.R.; Worthen, B.R. Program Evaluation: Alternative Approaches and Practical Guidelines, 4th ed.; Pearson PLC: London, United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland.
- Pit-ten Cate, I.M.; Hörstermann, T.; Krolak-Schwerdt, S.; Gräsel, C.; Böhmer, I.; Glock, Due south. Teachers' information processing and sentence accuracy: Effects of information consistency and accountability. Eur. J. Psychol. Educ. 2020, 35, 675–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkacheva, 1000.Five. Modeling the Practice-Oriented Content of Teaching Aids for Professional Education; Found of Education: Moscow, Russia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bryk, A.Southward. Improvement in Action: Advancing Quality in America's Schools (Continuous Improvement in Instruction Serial); Harvard Educational activity Press: Cambridge, MA, U.s.a., 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Stockard, J.; Woods, T.Due west.; Coughlin, C.; Khoury, C.R. All Students Can Succeed: A Half Century of Inquiry on the Effectiveness of Directly Instruction; Lexington Books: Lanham, Maryland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lagreca, G.F.; Kang, K. Meaningful integration of educational applied science in postgraduate programs: Trouble, solution, and results. J. Dent. Educ. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burlea-Schiopoiu, A.; Mihai, 1000.; Mihai, L. The leadership behaviour of the accounting students: A dilemma for college education. Int. J. Organ. Leadersh. 2016, 5, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlea-Schiopoiu, A. The Complexity of an eastward-Learning Organisation: A Prototype for the Human Factor; Springer: New York, NY, United states, 2009; Volume ii, pp. 267–278. ISBN 978-0-387-30403-8. [Google Scholar]
- Khoroshilov, A.A. Methods, Models, Algorithms, and Experimental Software for Automatic Detection of Implicit Borrowings in Scientific and Technical Texts. Ph.D. Thesis, Federal Research Centre Information science and Management of the Russian University of Sciences, Moscow, Russia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kolb, L. Learning Get-go, Engineering science 2d in Practice: New Strategies, Research and Tools for Educatee Success; International Gild for Technology in Didactics: Washington, DC, The states, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Melle, Due east. Van Using a Logic Model to Assist in the Planning, Implementation, and Evaluation of Educational Programs. Acad. Med. 2016, 91, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blinov, P.D. Method, Algorithms, and Software System for the Attribute-Emotional Assay of Texts. Ph.D. Thesis, Vyatka State University, Kirov, Russia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, P.S.; Adonis, T.-A. Quality Balls of Community Date in South African Higher Education Institutions: Problems and Prospects. Due south. Afr. Rev. Sociol. 2020, 51, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibb, G.S.; Dyches, T.T. IEPs: Writing Quality Individualized Education Programs; Pearson: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Muljana, P.S.; Nissenson, P.M.; Luo, T. Examining Factors Influencing Faculty Purchase-in and Involvement in the Accreditation Process: A Crusade Analysis Grounded in Systems Thinking. TechTrends 2020, 64, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işık, A. Practise Students Experience that they are Assessed Properly? Iran. J. Lang. Teach. Res. 2020, 8, 63–92. [Google Scholar]
- Afanaseva, E.A.; Ivanov, A.South.; Yankevich, V.B. The employers participation in the assessment of educational programs and graduate training. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Vi Forum Strategic Partnership of Universities and Enterprises of Hullo-Tech Branches (Science. Education. Innovations) (SPUE), St. Petersburg, Russia, fifteen–17 Nov 2017; pp. 33–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, S.M. Factors influencing the development of network educational programs betwixt Russian and Kyrgyz universities. Vestn. Tomsk. Gos. Univ. 2016, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, Fifty. Faculty Beliefs Apropos the Preparation of Physical Education Teacher Teaching Students for Advisable Practices. Phys. Educ. 2020, 77, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudin, M.Due north.; Bezbakh, V.V.; Frolova, E.Eastward.; Galkina, M.V. The Models of College Pedagogy in Russian federation and European Countries at the beginning of the XXIst century: The Primary Directions of Development. Eur. J. Contemp. Educ. 2018, vii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarides, R.; Watt, H.One thousand.G.; Richardson, P.W. Teachers' classroom management self-efficacy, perceived classroom direction and teaching contexts from beginning until mid-career. Learn. Instr. 2020, 69, 101346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, L.K.A.; Segura, G.N.R.; Vera, Chiliad.C.T.; Olvera, M.A.Z.; Noda, S. the integration of systems, programs, plans, projects and strategies for the achievement of educational quality. Rev. Univ. Soc. 2020, 12, 426–435. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez, J.G.1000.; Amaya, A.A. Design of online subjects through the competency model for educational programs "due east-Learning". Campus Virtuales 2016, 2, xxx–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, C.; Zhang, X. Improving MOOC learning performance in China: An analysis of factors from the TAM and TPB. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 2020, 28, 1421–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logachev, G.; Tkacheva, M.; Samarin, Y. Educational Program as a Tool of the Quality Management System of Vocational Instruction; INFRA-M Academic Publishing LLC.: Moscow, Russia, 2019; ISBN 978-5-16-014934-nine. [Google Scholar]
- Logachev, Yard.S.; Samarin, I.N.; Vinokurova, O.A. Integralnyi pokazatel kachestva obrazovatelnykh programm [Integral indicator of the quality of educational programs]. XXI Vek Itogi Proshlogo Probl. Nastoiashchego Plius 2019, 8, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Logachev, M.Due south.; Zhukova, G.S. Problems of professional education in Russia: Quality monitoring of educational programs. Rev. Incl. 2020, 7, 263–274. [Google Scholar]
- Dasheev, D.E. Automatic Educational System as a Ways of Formation of Professional Competencies in Future Engineers. Ph.D. Thesis, Buryat State Academy, Ulan-Ude, Russia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Topper, A.; Lancaster, S. Online graduate educational technology program: An illuminative evaluation. Stud. Educ. Eval. 2016, 51, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diusekeev, K.A. Managing the Effectiveness of University Enquiry and Education Staff. Ph.D. Thesis, Astrakhan Land University, Astrakhan, Russia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vinokurova, O.A. Identification of Automatic Data Processing Processes in the Printing Industry. Ph.D. Thesis, Moscow State University of Press Arts, Moscow, Russia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Vinokurova, O.A.; Efimov, One thousand.V.; Samarin, Y.N.; Sinyak, Thou.A. Methods and Means of Information Processing in Prepress Systems; Moscow State Academy of Press Arts: Moscow, Russia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov, I.A. Car Learning Methods and Algorithms for Processing and Classification of Semi-Structured Text. Ph.D. Thesis, National Inquiry Nuclear University MEPhI, Moscow, Russia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Luniashin, I.V. Inquiry and Development of Methods for Organizing the Execution of Data Processes in Altitude Learning. Ph.D. Thesis, Moscow Technical Academy of Communications and Informatics, Moscow, Russia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
Effigy 1. Documents determining the content of an educational program.
Effigy i. Documents determining the content of an educational programme.
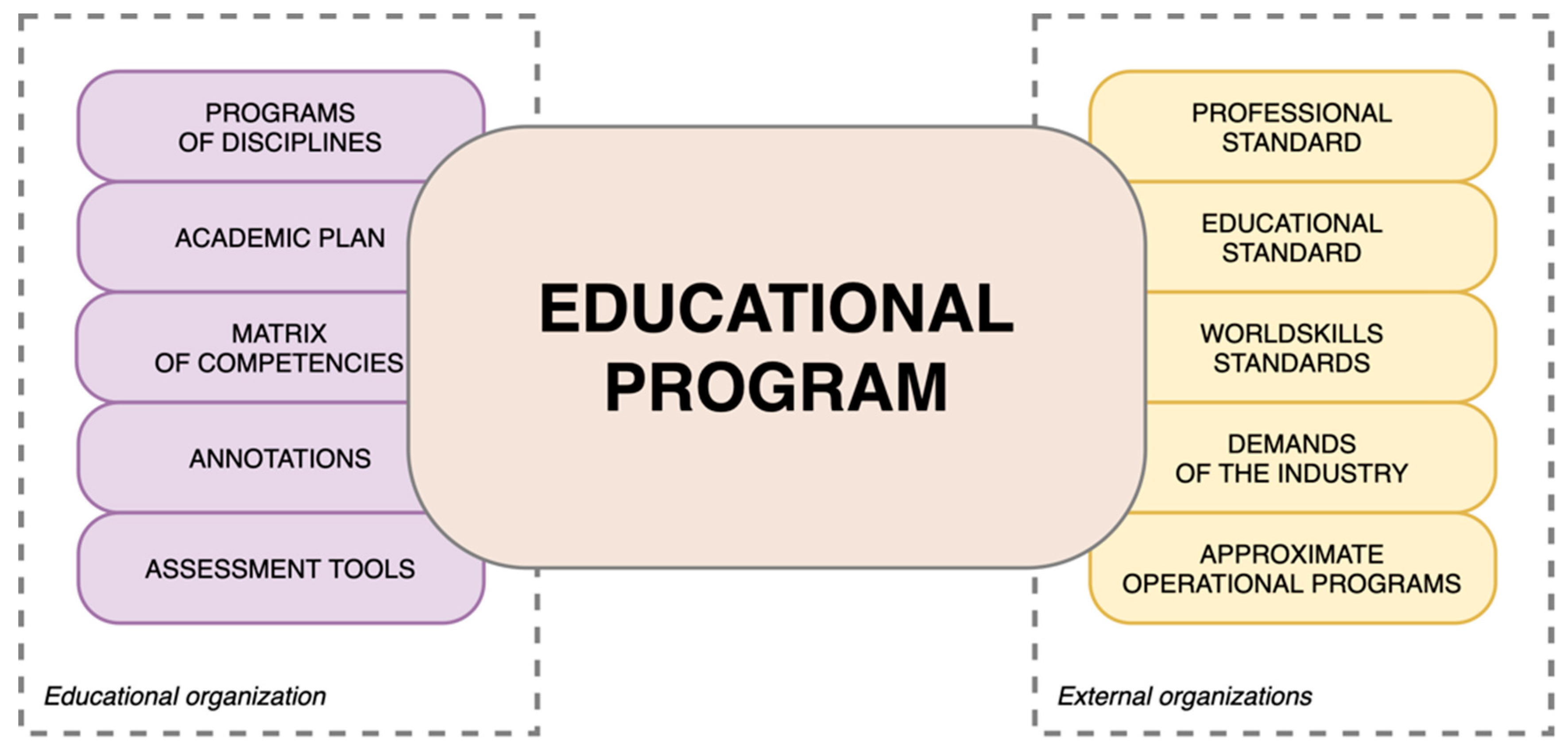
Figure two. Structural elements of an educational plan.
Figure 2. Structural elements of an educational program.
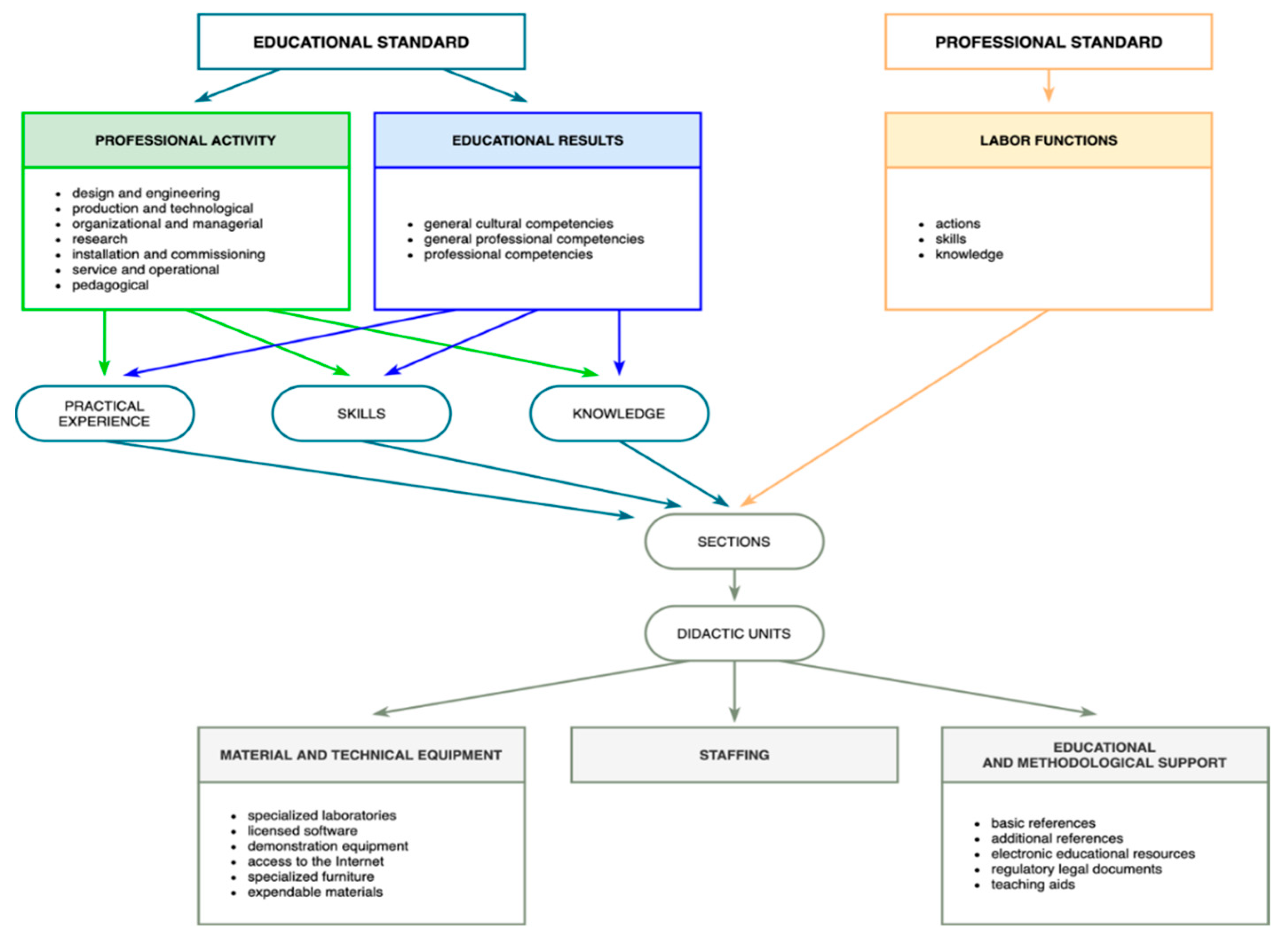
Figure 3. The structure of an information arrangement for monitoring and managing the quality of educational programs.
Figure iii. The construction of an information system for monitoring and managing the quality of educational programs.

Figure 4. The example of a diagram obtained as a upshot of aspect assessment.
Figure four. The instance of a diagram obtained as a result of attribute assessment.
Effigy 5. Entity–relationship (ER) model of data from the database of the information system for monitoring the quality of educational programs.
Figure 5. Entity–relationship (ER) model of data from the database of the data system for monitoring the quality of educational programs.
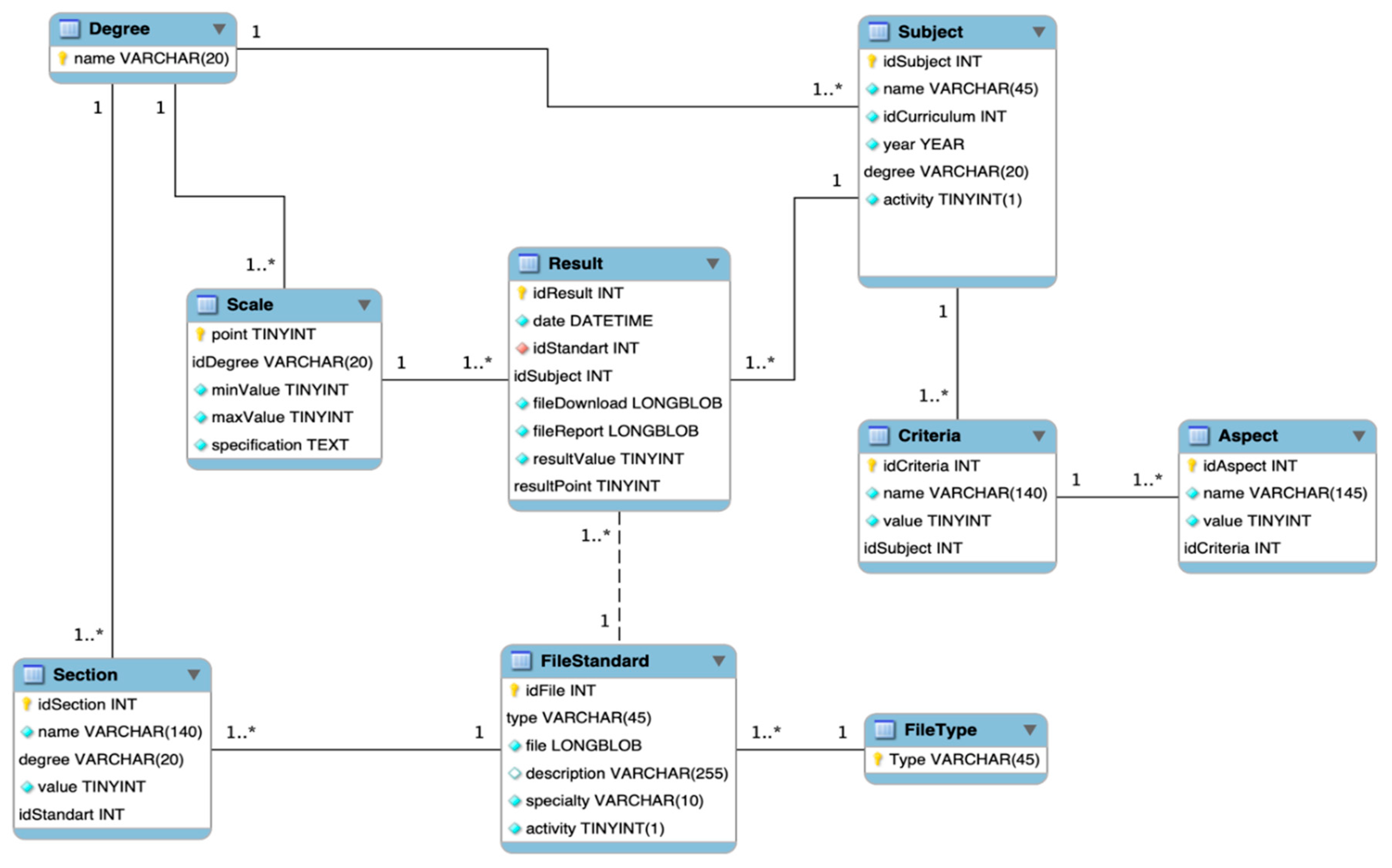
Figure half-dozen. Consequence-driven process chain of the process of assessing the formal role of a fragment of an educational program.
Figure six. Event-driven process chain of the process of assessing the formal part of a fragment of an educational program.

Tabular array i. A fragment of the results of expert evaluation of the significance of criteria of educational programme quality evaluation.
Table i. A fragment of the results of expert evaluation of the significance of criteria of educational program quality evaluation.
| №. | Criterion | Aspect | Value, % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| of the Aspect | of the Criterion | |||
| 1 | The passport of programs of educational disciplines is filled in correctly | Corresponds to the template | 8.1 | nine.5 |
| two | The type of professional action is indicated correctly | half-dozen.4 | ||
| iii | Professional competencies are indicated correctly | 17.three | ||
| 4 | General cultural and general professional competencies are indicated correctly | 17.iii | ||
| 5 | Knowledge is indicated correctly | eleven.4 | ||
| 6 | Skills are indicated correctly | 11.iv | ||
| seven | Practical experience is indicated correctly | eleven.iv | ||
| 8 | The indicated number of bookish hours corresponds to the academic plan | xvi.7 | ||
| 9 | The contrary side of the title page is filled in | Corresponds to the educational standard | eight.5 | 14.5 |
| 10 | The educational program is approved | 23.7 | ||
| 11 | The educational program is confirmed | 27.nine | ||
| 12 | The educational plan is authorized | 18.three | ||
| 13 | The columns "Author/Compiler" are filled in correctly | 12.eight | ||
| 14 | The form completion corresponds to the template | 8.8 | ||
| Publisher'south Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 past the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This commodity is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Eatables Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
DOWNLOAD HERE
Posted by: judymariust.blogspot.com